Quadratic Voting
Quadratic Voting (QV) is a redesigned voting method reflecting the intensity of people’s preferences in collective decisions. It greatly mitigates tyranny-of-the-majority and factional control problems.
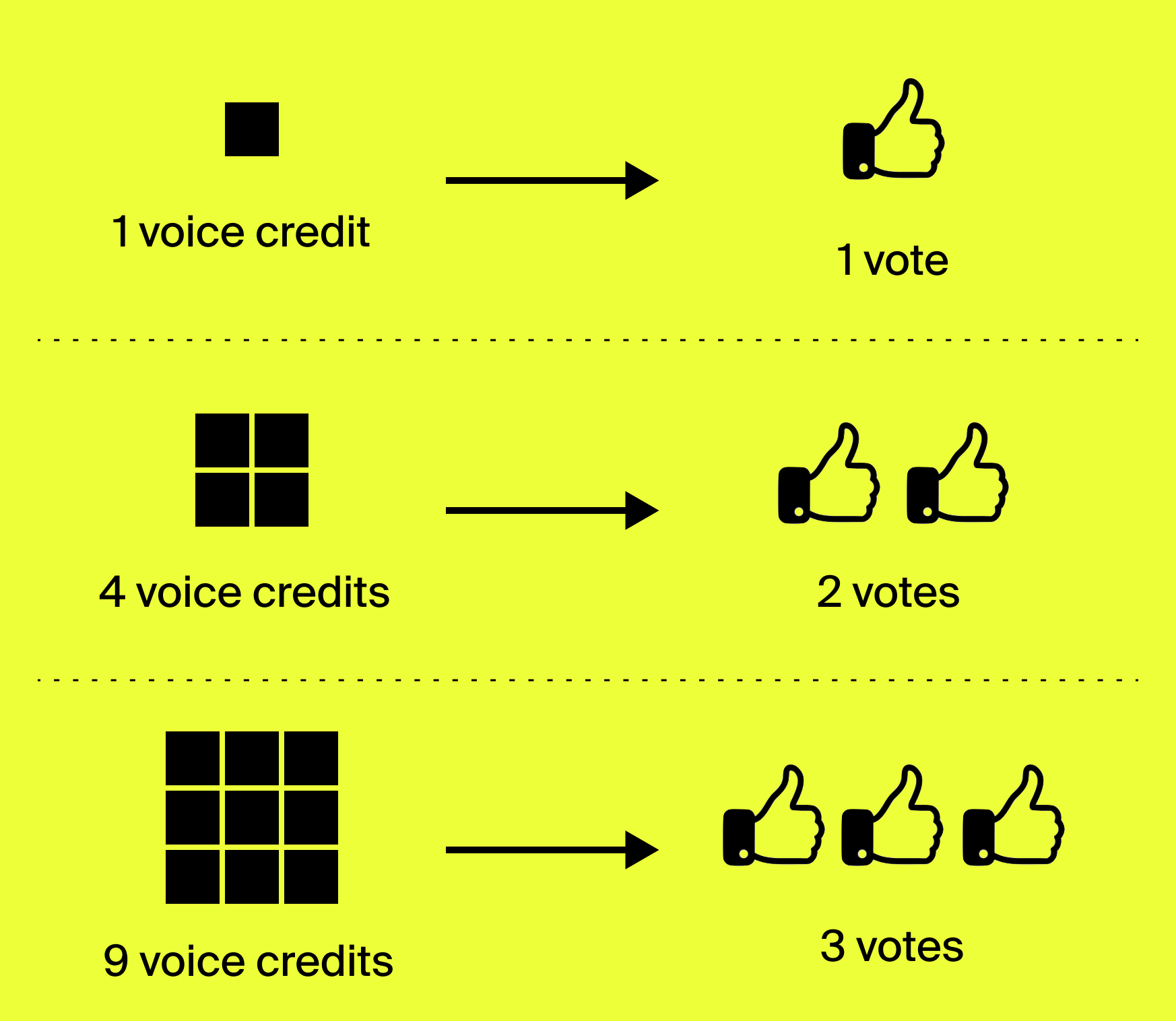
Voters receive budgets of “voice credits,” which they allocate to different questions on the ballot to signal the intensity of their conviction. Their voice credits convert to “counted votes” according to their square root. So if you put one voice credit on an issue, that is one vote; four credits are two votes; nine credits are three votes, and so on.
Use cases
Prioritization, Roadmapping, and Budgeting
Quadratic Voting is a great tool for prioritizing proposals that draw from a common, finite resource. For example, if a group needs to decide on how to allocate a fixed budget across a set of proposed projects, QV provides a way to batch all the proposals onto a single ballot and efficiently gather rich data about which proposals the group cares about the most.
QV also shines in situations where the proposals draw on the group’s resources in ways that are harder to quantify. Sometimes the group needs to decide between different ways they can allocate their limited time and energy, such as in a product roadmap or a meeting agenda.
Polling and market research
Polling and market research represents another nuanced and powerful use case for QV. In a survey or opinion poll, individual respondents are battling for the attention of the group. Therefore, respondents are incentivized to “shout,” or express strong views.
Consider the widely used Likert survey format, in which respondents are asked to express how they feel about various issues on a scale of “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree.” In Likert surveys, responses tend to cluster to the extremes. As a result, these surveys tend to misrepresent the preferences of the group and magnify polarization.
Quadratic Voting gives everyone equal power to direct the attention of the group toward an issue they care about, but forces them to do so at the cost of their influence on other issues. In other words, individuals have a fixed amount of “voice”—and shouting about an issue will leave one with significantly less voice to use on other issues.
Case Studies
-
RadicalxChange Community Polls
Variations
- Plural Voting
Further Reading
A Decision Theoretic Approach to Understanding Survey Response: Likert vs. Quadratic Voting for Attitudinal Research - Charlotte Cavaillé et al.
A New Consensus Protocol: Quadratic Voting with Multiple Alternatives - Jon X. Eguia, Nicole Immorlica, Katrina Ligett, Glen Weyl, Dimitrios Xefteris
Agent-Based Models of Quadratic Voting - Jacob Kelter, Andreas Bugler, Uri Wilensky
Agonistics: Thinking The World Politically - Chantal Mouffe
Between Abundance and Scarcity - Matt Prewitt
Chapter 2 of Radical Markets - Eric A. Posner, E. Glen Weyl
Democracy Squared - Eric A. Posner, E. Glen Weyl
Experimental Voting Effort Aims to Break Ethereum Governance Gridlock - Rachel Rose O’Leary
How does the ‘Quadratic voting’ find the next step for democracy in the blockchain community? - pupupupuisland
On Collusion - Vitalik Buterin
Quadratic Voting and the Public Good: Introduction - Eric A. Posner, E. Glen Weyl
Quadratic Voting: A New Way to Govern Blockchains for Enterprises - Sherman Lee
Quadratic Voting in Colorado: 2020 - Leon Erichsen, Matt Prewitt
Quadratic Voting in the Wild - David Quarfoot et al.
QV or Not QV? That is the Question: Some Skepticism about Radical Egalitarian Voting Markets - Richard L. Hasen
QV Polling Method Gains Steam in Colorado State Legislature - Alex Randaccio, Eli Zeger
Storable Votes and Quadratic Voting, an Experiment on Four California Propositions - Alessandra Casella, Luis Sanchez
The Handbook for Radical Local Democracy - Matt Prewitt, Paul Healy
Towards a Connected Society - Danielle Allen
Tools
RxC QV - RadicalxChange’s in-house Quadratic Voting tool. Use this tool to create elections, send unique invite links to voters, and view results in a sleek and simple interface.
Government Technology Agency (Singapore) - Another great choice for doing a casual Quadratic Vote with your peers. It is all straightforward from election creation, email / link invites, and quadratic voting to result analysis. You can even build your own interface on top of it using the associated APIs.
Sheets Template for Quadratic Voting - Have small scale Quadratic Votes in mind? These sheets might be just right for you. It’s a buch of interconnected columns and rows that let you easily perform and analyze Quadratic Votes in line with your needs. Dive into the folder, make a copy of the files, and off you go!
Quadratic Moloch DAO / Democracy Earth - Quadratic Moloch DAO is a fork from the Moloch DAO smart contract standard that incorporates the optional use of Quadratic Voting. Moloch DAOs let collectives manage different kinds of rights and assets through democratic processes on Ethereum.
CultureStake / Furtherfield - CultureStake’s playful Quadratic Voting app allows you to vote on the types of cultural activity you would like to see in your locality. It democratizes arts commissioning by providing communities and artists with a radical tool to make cultural decisions together.